2.2.3
随着人们健康意识的增强,越来越多的人开始关注日常运动和健康管理。使用提供的训练数据,补全2.2.3.ipynb代码。选择合适的特征,开发一个预测模型,基于个体性别,个体对运动的看法和个人健康评价来预测个体年龄。利用测试工具对模型进行测试,并对测试结果进行分析,完成测试报告,并运用工具对错误原因进行纠正。
详细说明如下:
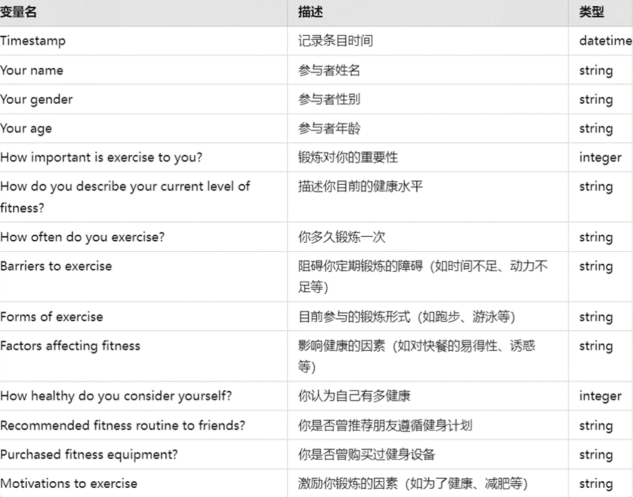
(1)正确加载数据集,并显示前五行的数据
(2)使用随机森林模型进行模型训练,要求设定自变量和因变量,并根据自变量特征进行模型训练,最终将训练好的模型以文件名2.2.3_model.pkl保存到考生文件夹,结果文件以2.2.3_results.txt保存到考生文件夹。
(3)使用测试工具对模型进行测试,并记录测试结果,命名2.2.3_report.txt,保存到考生文件夹
(4)对测试结果进行详细分析,并编写测试报告,包括模型性能评估、错误分析及改进建议,将答案写到答题卷文件中,答题卷文件命名为“2.2.3.docx”,保存到考生文件夹。
(5)运用工具分析算法中错误案例产生的原因并进行纠正,重新得到模型训练结果,以文件名2.2.3_results_xgb.txt保存到考生文件夹。
(6)将以上代码以及运行结果,以html格式保存并命名为2.2.3.html,保存到考生文件夹,考生文件夹命名为“准考证号+身份证后6位”。
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
import pickle
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
import xgboost as xgb
# 加载数据集
df = __________
# 显示前五行数据
print(__________)
# 去除所有字符串字段的前后空格
df = df.applymap(lambda x: x.strip() if isinstance(x, str) else x)
# 检查和清理列名
df.columns = df.columns.str.strip()
# 选择相关特征进行建模
X = df[['Your gender', 'How important is exercise to you ?', 'How healthy do you consider yourself?']]
X = __________(X) # 将分类变量转为数值变量
# 将年龄段转为数值变量
y = __________(lambda x: int(x.split(' ')[0])) # 假设年龄段为整数
# 将数据集划分为训练集和测试集(测试集占比20%)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = __________(__________, random_state=42)
# 创建随机森林回归模型(创建的决策树的数量为100)
rf_model = __________(__________, random_state=42)
# 训练随机森林回归模型
__________
# 保存训练好的模型
with open('2.2.3_model.pkl', 'wb') as model_file:
pickle.__________
# 进行结果预测
y_pred = __________
results_df = pd.DataFrame(y_pred, columns=['预测结果'])
results_df.to_csv('2.2.3_results.txt', index=False)
# 使用测试工具对模型进行测试,并记录测试结果
train_score = __________ #训练集分数
test_score = __________ #测试集分数
mse = __________ #均方误差
r2 = __________ #决定系数
with open('2.2.3_report.txt', 'w') as report_file:
report_file.write(f'训练集得分: {train_score}\n')
report_file.write(f'测试集得分: {test_score}\n')
report_file.write(f'均方误差(MSE): {mse}\n')
report_file.write(f'决定系数(R^2): {r2}\n')
# 运用工具分析算法中错误案例产生的原因并进行纠正
# 初始化XGBoost回归模型(构建100棵树)
xgb_model = __________(__________, random_state=42)
# 训练XGBoost回归模型
__________
# 使用XGBoost回归模型在测试集上进行结果预测
y_pred_xgb = __________
results_df_xgb = pd.DataFrame(y_pred_xgb, columns=['预测结果'])
results_df_xgb.to_csv('2.2.3_results_xgb.txt', index=False)
with open('2.2.3_report_xgb.txt', 'w') as xgb_report_file:
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost训练集得分: {__________}\n')
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost测试集得分: {__________}\n')
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost均方误差(MSE): {__________}\n')
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost决定系数(R^2): {__________)}\n')
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
import pickle
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
import xgboost as xgb
# 加载数据集
df = pd.read_csv('fitness analysis.csv')
# 显示前五行数据
print(df.head(5))
# 去除所有字符串字段的前后空格
df = df.applymap(lambda x: x.strip() if isinstance(x, str) else x)
# 检查和清理列名
df.columns = df.columns.str.strip()
# 选择相关特征进行建模
X = df[['Your gender', 'How important is exercise to you ?', 'How healthy do you consider yourself?']]
X = pd.get_dummies(X) # 将分类变量转为数值变量
# 将年龄段转为数值变量 这里只有一列,所以用apply
y = df['Your age'].apply(lambda x: int(x.split(' ')[0])) # 假设年龄段为整数
# 将数据集划分为训练集和测试集(测试集占比20%)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建随机森林回归模型(创建的决策树的数量为100)
rf_model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
# 训练随机森林回归模型
rf_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 保存训练好的模型
with open('2.2.3_model.pkl', 'wb') as model_file:
pickle.dump(rf_model, model_file)
# 进行结果预测
y_pred = rf_model.predict(X_test)
results_df = pd.DataFrame(y_pred, columns=['预测结果'])
results_df.to_csv('2.2.3_results.txt', index=False)
# 使用测试工具对模型进行测试,并记录测试结果
train_score = rf_model.score(X_train, y_train) #训练集分数
test_score = rf_model.score(X_test, y_test) #测试集分数
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred) #均方误差 求预测值和真实之的差异
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred) #决定系数
with open('2.2.3_report.txt', 'w') as report_file:
report_file.write(f'训练集得分: {train_score}\n')
report_file.write(f'测试集得分: {test_score}\n')
report_file.write(f'均方误差(MSE): {mse}\n')
report_file.write(f'决定系数(R^2): {r2}\n')
# 运用工具分析算法中错误案例产生的原因并进行纠正
# 初始化XGBoost回归模型(构建100棵树)
xgb_model = xgb.XGBRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
# 训练XGBoost回归模型
xgb_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 使用XGBoost回归模型在测试集上进行结果预测
y_pred_xgb = xgb_model.predict(X_test)
results_df_xgb = pd.DataFrame(y_pred_xgb, columns=['预测结果'])
results_df_xgb.to_csv('2.2.3_results_xgb.txt', index=False)
with open('2.2.3_report_xgb.txt', 'w') as xgb_report_file:
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost训练集得分: {xgb_model.score(X_train, y_train)}\n')
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost测试集得分: {xgb_model.score(X_test, y_test)}\n')
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost均方误差(MSE): {mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_xgb)}\n')
xgb_report_file.write(f'XGBoost决定系数(R^2): {r2_score(y_test, y_pred_xgb)}\n')
print(f'XGBoost训练集得分: {xgb_model.score(X_train, y_train)}\n')
print(f'XGBoost测试集得分: {xgb_model.score(X_test, y_test)}\n')
print(f'XGBoost均方误差(MSE): {mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_xgb)}\n')
print(f'XGBoost决定系数(R^2): {r2_score(y_test, y_pred_xgb)}\n')
运行结果
Timestamp ... What motivates you to exercise? (Please select all that applies )
0 2019/07/03 11:48:07 PM GMT+5:30 ... I'm sorry ... I'm not really interested in exe...
1 2019/07/03 11:51:22 PM GMT+5:30 ... I want to be fit;I want to be flexible;I want ...
2 2019/07/03 11:56:28 PM GMT+5:30 ... I want to be fit
3 2019/07/04 5:43:35 AM GMT+5:30 ... I want to be fit;I want to lose weight
4 2019/07/04 5:44:29 AM GMT+5:30 ... I want to be fit
[5 rows x 18 columns]
/var/folders/rq/lzp3p28j4wsfzc34n6x5rdlh0000gn/T/ipykernel_52546/1394302798.py:15: FutureWarning: DataFrame.applymap has been deprecated. Use DataFrame.map instead.
df = df.applymap(lambda x: x.strip() if isinstance(x, str) else x)
XGBoost训练集得分: 0.12619709968566895
XGBoost测试集得分: -0.09105539321899414
XGBoost均方误差(MSE): 109.65194073026862
XGBoost决定系数(R^2): -0.09105539321899414